Python Refresher
Click here to jump straight to notebook.
Welcome Pythonists
Python is a general-purpose, versatile and popular programming language.
It's great as a first language as it is simple and easy to read, and it is also a good language to have in any programmer's stack as it can be used for everything from web development to software development and scientific applications..
Organizations using Python include
- IBM
- CIA
- NASA
- Quora
- Yahooo
- Dropbox
- YouTube
- UCL Irvine
To find what Python is all about, explore some of the links below:
- What is Python? Executive Summary
- Compare Python with other languages
- Python (programming language) - Wikipedia
- Python Success Stories
- What is the most famous software written in Python? - Quora Post
- Collection of short programs, which show off Python's syntax and readability
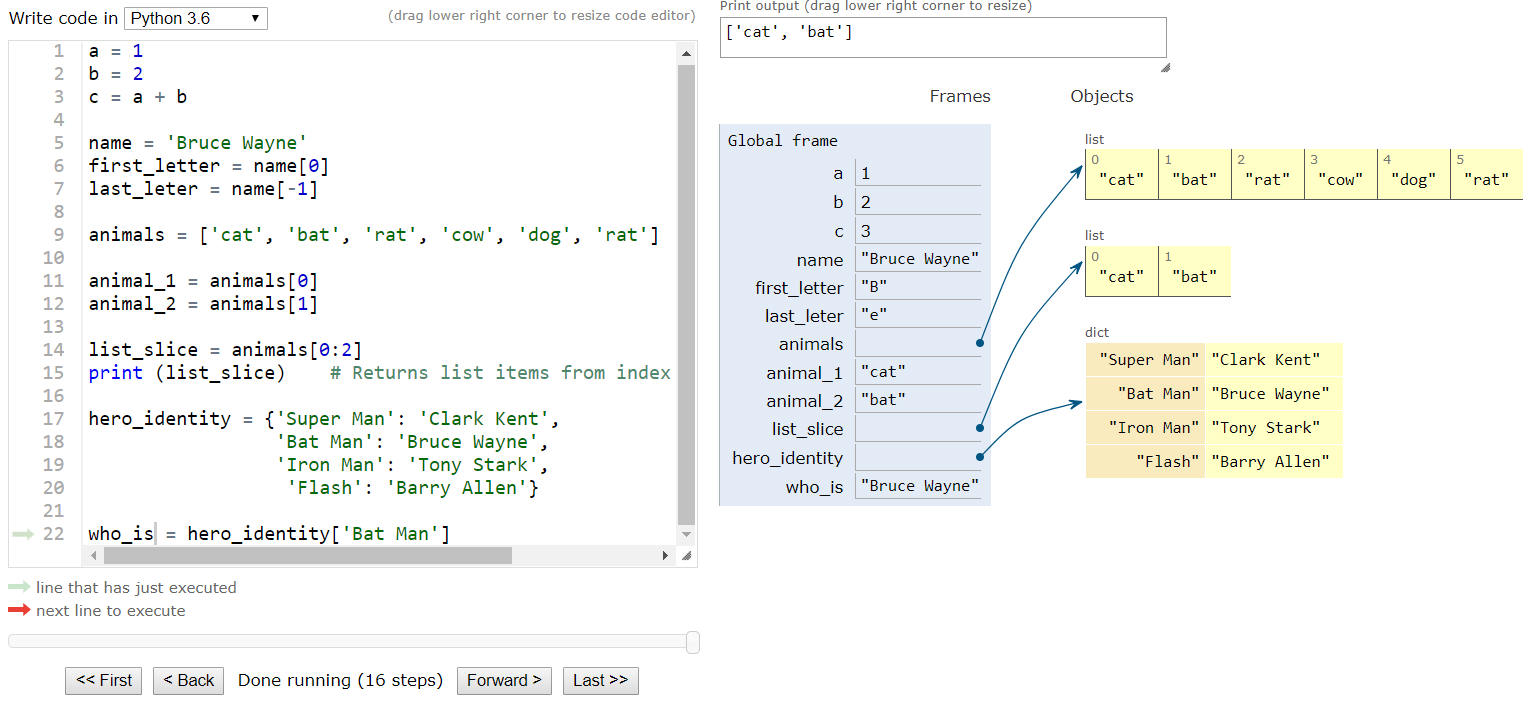
Visit Python Tutor Visualizer to visualise the code and understand what happens behind the screen when each line of Python code runs. It shows the assignment of all the variables and the variale scopes graphically as shown below.
IDLE Installation (optional)
If you alread have IDLE or other development IDE's, you can skip installing IDLE.
Visit https://www.python.org/downloads/ to download and install latest version of python with IDLE. As of writing this page, the latest version is Python 3.7.0. IDLE Shell will look something like the image below (We can customise the environment to suit our taste).
Time for Fun
Without talking any further, let's dive straight into the program and have some fun. Run the code below
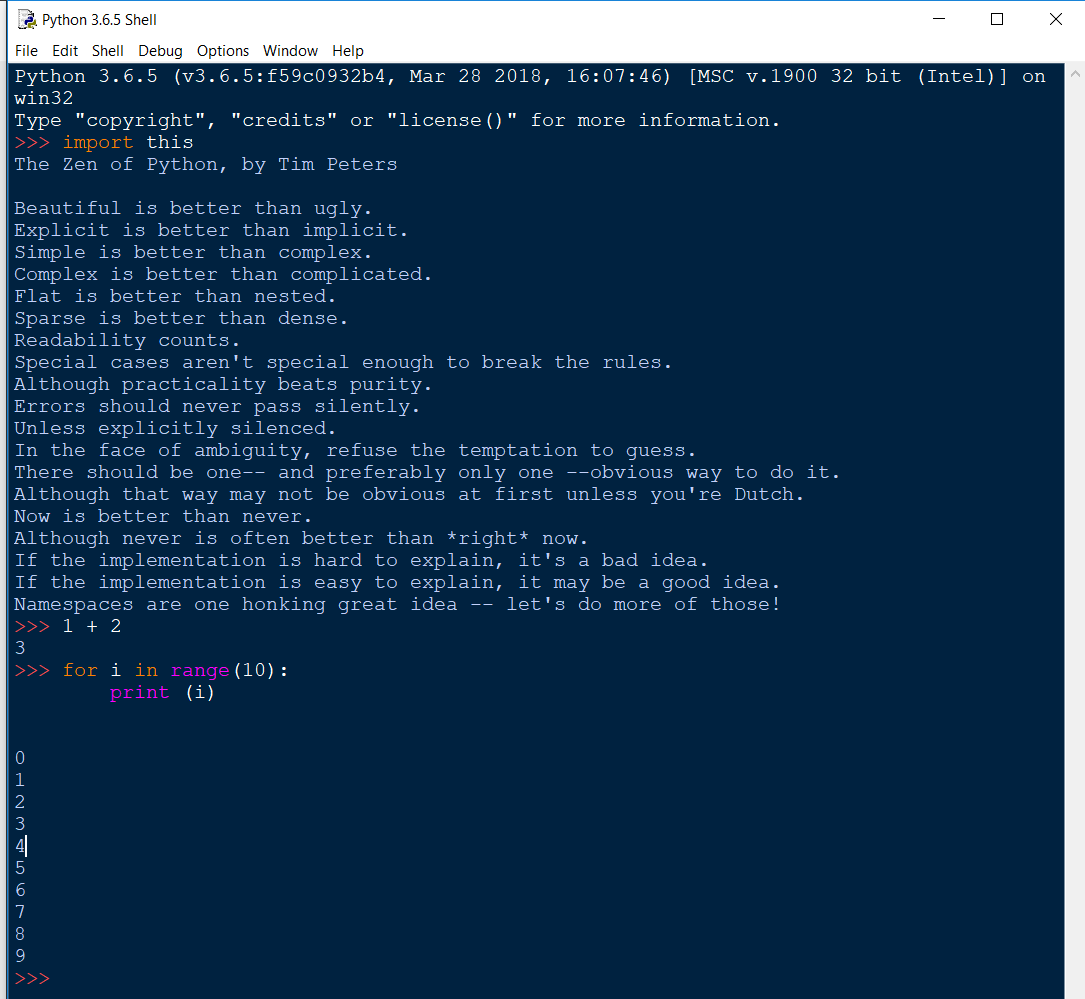
import this
and you will see the output as shown below. The Zen of Python is a collection of 20 software principles that influences the design of Python Programming Language.
It is included as an easter egg in the Python interpreter, which can be displayed by entering import this
The Zen of Python, by Tim Peters Beautiful is better than ugly. Explicit is better than implicit. Simple is better than complex. Complex is better than complicated. Flat is better than nested. Sparse is better than dense. Readability counts. Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules. Although practicality beats purity. Errors should never pass silently. Unless explicitly silenced. In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess. There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it. Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch. Now is better than never. Although never is often better than *right* now. If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea. If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea. Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!
If you run the code below
print (this.s)
and you will see the output as shown below. Here, the Zen of Python is ceaser chipered by 13 places.
For more details on import this module, ceaser chiphering & ROT-13,
refer wikipedia or
stack overflow.
Gur Mra bs Clguba, ol Gvz Crgref Ornhgvshy vf orggre guna htyl. Rkcyvpvg vf orggre guna vzcyvpvg. Fvzcyr vf orggre guna pbzcyrk. Pbzcyrk vf orggre guna pbzcyvpngrq. Syng vf orggre guna arfgrq. Fcnefr vf orggre guna qrafr. Ernqnovyvgl pbhagf. Fcrpvny pnfrf nera'g fcrpvny rabhtu gb oernx gur ehyrf. Nygubhtu cenpgvpnyvgl orngf chevgl. Reebef fubhyq arire cnff fvyragyl. Hayrff rkcyvpvgyl fvyraprq. Va gur snpr bs nzovthvgl, ershfr gur grzcgngvba gb thrff. Gurer fubhyq or bar-- naq cersrenoyl bayl bar --boivbhf jnl gb qb vg. Nygubhtu gung jnl znl abg or boivbhf ng svefg hayrff lbh'er Qhgpu. Abj vf orggre guna arire. Nygubhtu arire vf bsgra orggre guna *evtug* abj. Vs gur vzcyrzragngvba vf uneq gb rkcynva, vg'f n onq vqrn. Vs gur vzcyrzragngvba vf rnfl gb rkcynva, vg znl or n tbbq vqrn. Anzrfcnprf ner bar ubaxvat terng vqrn -- yrg'f qb zber bs gubfr!
To decrypt the above encoded module, you can run one of the 2 codes shown below.
import codecs
print (codecs.decode(this.s, 'rot13'))
print ("".join([this.d.get(c, c) for c in this.s]))
Installing packages using pip
Pip is a package manager used to install and manage softwares written in Python. You can access the pip from command prompt or terminal.
To check the pip version
pip -V

To check whether a package is already installed
pip show package_name
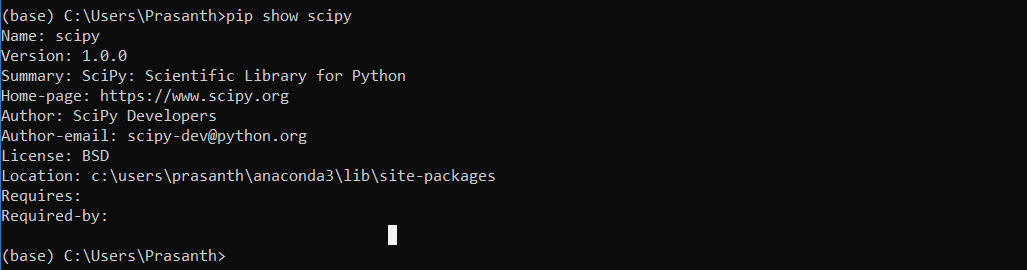
If the package doesnt exist, it will show nothing

To install a new package
pip install package_name
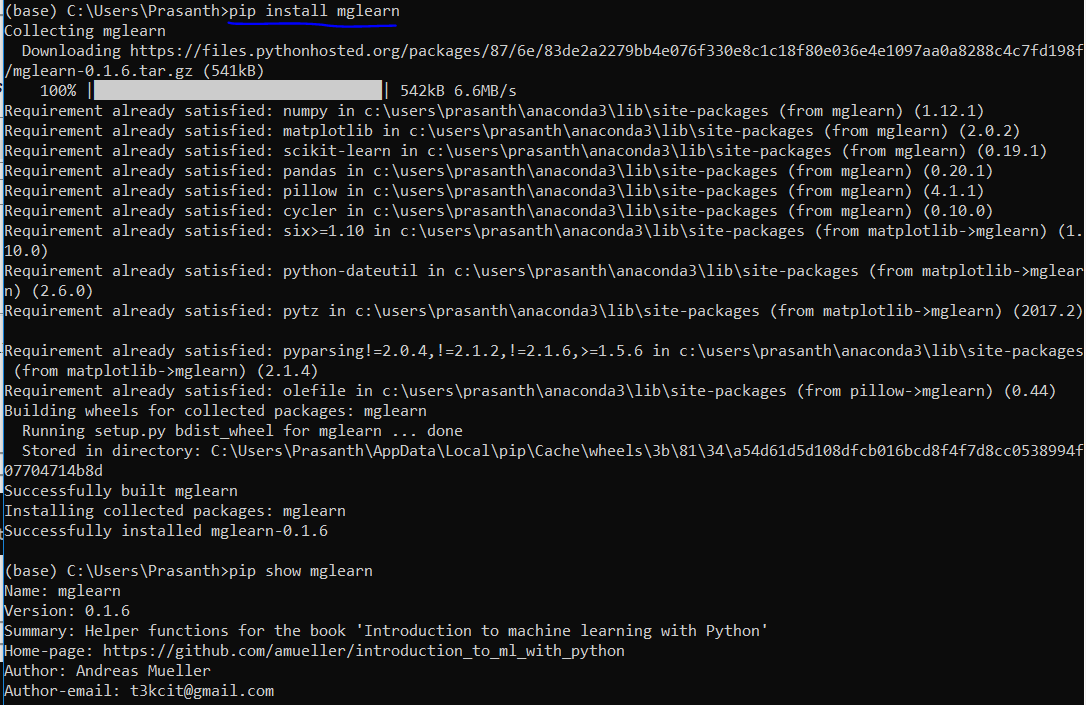
Python Packages used in this course
Mandatory pacakges
- numpy
- matplotlib
- sklearn
- scipy
- pandas
- mglearn
- graphviz
- tensorflow
Optional packages
- matplotlib-venn
- seaborn
Python Refresher - Notebook
For Nerds and Geeks - Computer Hardware Architecture
Before we start learning the Python programming language to give instructions to computers, let's have a sneak peek of how computers are built. If you were to rip off a computer or cell phone and look deep inside, we would find the following parts:
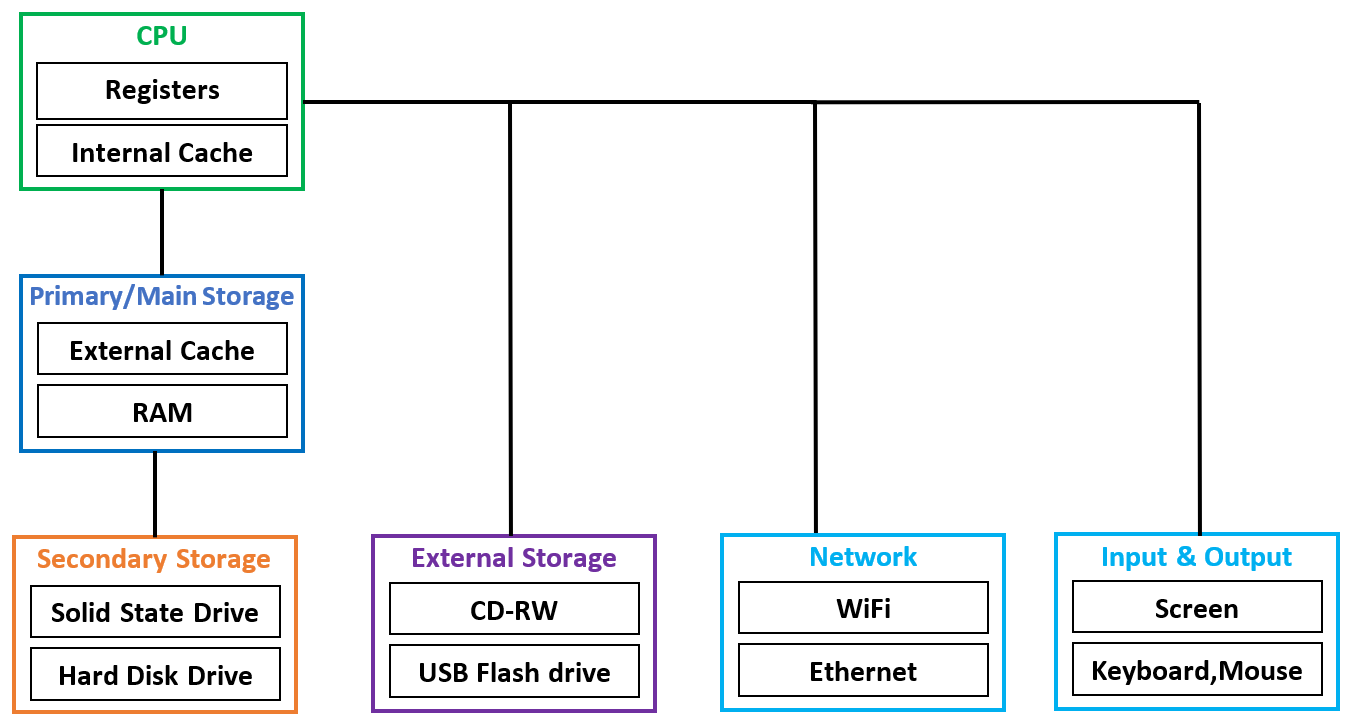
Central Processing Unitis where our program is executed. It's obsessed with "what's next". If our computer is rated at 1 GHz, it will ask "what's next" 1 million times per second. i.e. runs one million instructions / sec.Main Memoryis used to store information that CPU needs in a hurry. Data and programs currently in use are stored in RAM. Their drawback is info stored in it vanishes when the computer is turned off.Secondary Memoryis also used to store information, but it is much slower than the main memory. Data and program files are usually stored in Hard Disk. The advantage of the secondary memory is that it can store information even when there is no power to the computer and are usually cheaper than RAM & offer more storage space.Network Connectionis used to retrieve information over internet or intranet. We can think of the network as a very slow place to store and retrieve data that might not always be "up". So in a sense, the network is a slower and at times unreliable form of Secondary Memory. However, the recent advancements in fibre optics enabled widespread access to network speed of 1 Gbps & more. Transferring data between the servers will be atleast 100MB/s and will be faster than USB3.0.Input & Output devicesare simply our screen, keyboard, mouse, microphone, speaker, touchpad, etc. They are all of the ways we interact with the computer.
As a programmer, we will mostly be "talking" to the CPU and telling it what to do next by writing down instructions.
We call these stored instructions a program and the act of writing these instructions down is called as programming.
For Further reading
- Learn More Python - Learning resources for starters and intermediates in Python
- Automate the Boring Stuff with Python - Practical programming for total beginners, by Al Sweigart
- Learn Python - Interactive Online Tutorial from CodeCademy
- Python for Everybody - 5 course Specialization from Coursera by Prof Charles Severance, Univeristy of Michigan
- Python for Everybody Book - Written by Prof Charles Severance which provides an Informatics-oriented introduction to programming to solve real problems using Python.
- Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Using Python - by MIT Instructors in edX
- A Primer for Computational Biology
- Project Euler - To practice our coding skills
- Python and Data Science - Trello Public Sticky notes/li>